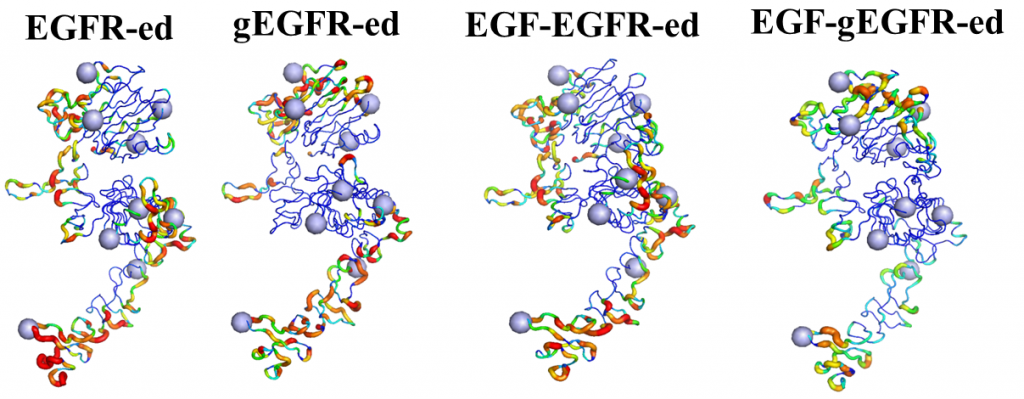
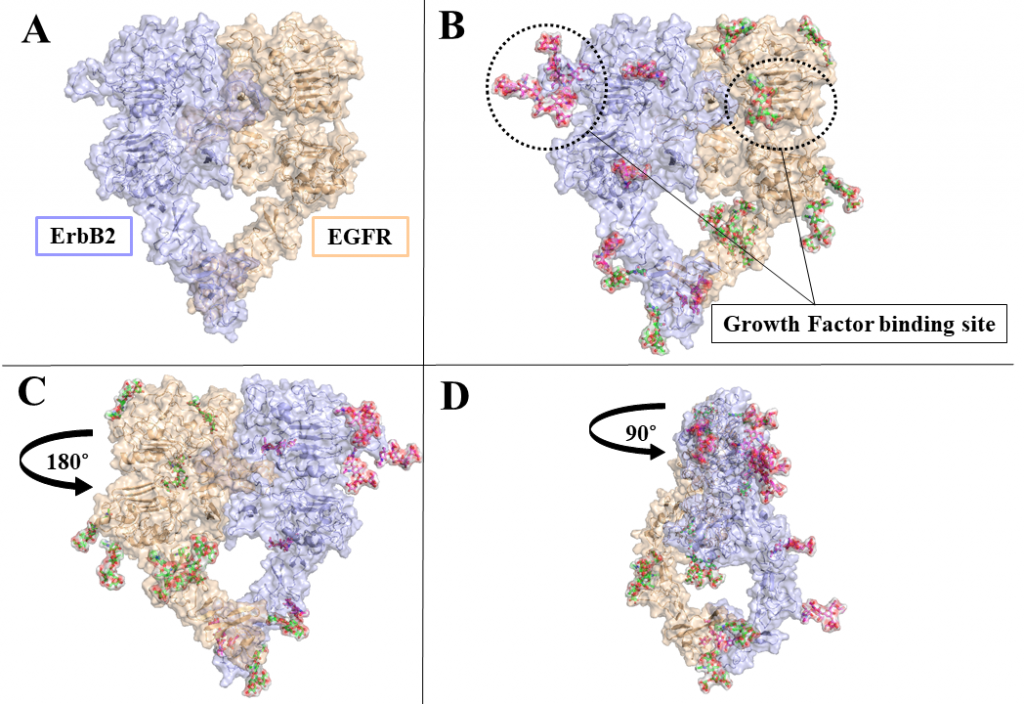
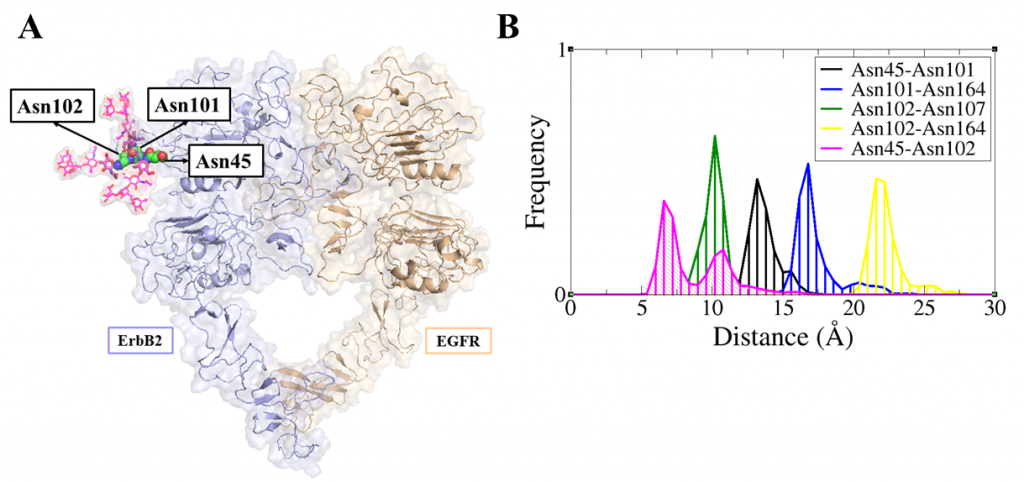
ErbB receptors are tyrosine kinase glycoproteins, overexpressed in several cancers. Their activation triggers various signaling cascades in the cytosol associated with cell proliferation and differentiation. ErbB receptors are activated by binding of growth hormone to their extracellular domain. Activated ErbB receptors form a back to back extended dimer on the cell surface. Various antibodies have been designed to inhibit ErbBs by targeting the growth factor binding site or the dimeric interface. Glycosidically bonded oligosaccharides to ErbBs extracellular domain are known to play a complex role in this activation process. I use molecular dynamics simulations to investigate the role of glycosylation in ErbB receptors functioning.